61. Rotate List
Rotate List
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
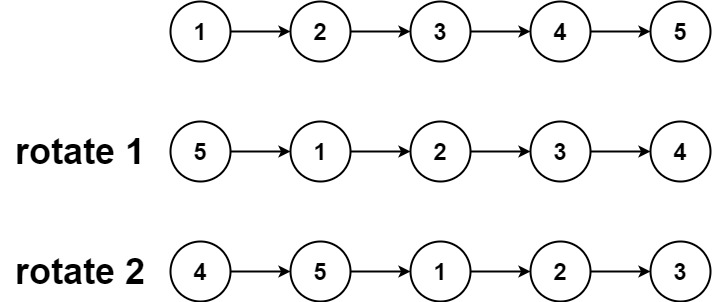
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
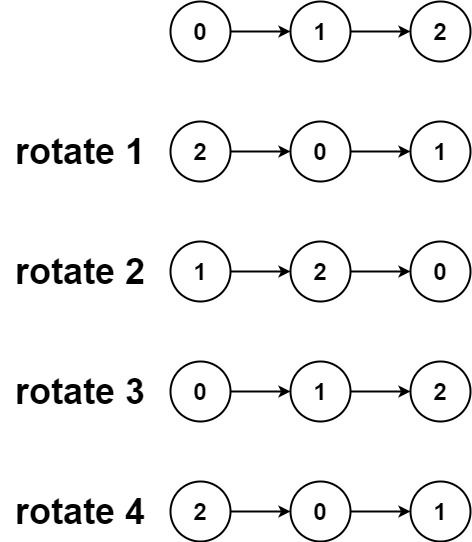
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Core strategy
For this problem, in short words, we need to move the last k nodes to the start of the linked list. So, what we need to do is:
- find the node of the current tail
- find the node before
knodes as the new tail - link the current tail to the original head
- link the new tail to
null
But there's something else we need to take care:
- we don't know the length of the linked list
- the linked list could be empty
- the
kcould be bigger than the length - the
kcould be 0 or the multiple of the length
So, for step 1, we could traverse the linked list to find the current tail. And during this, we could get the length of the linked list.
For step 2, we could calculate the index of that node by length and k, so what we need to do is traverse again.
For steps 3 and 4, we just need to change the value of next pointer.
With extra space
If we could use extra space, we may just put each node of the linked list into an array. And with the length and k, we could easily calculate the index and get what we want. Just take care of some corner cases.
Here's a sample code from me:
const rotateRight = (head, k) => {
if (!head || !head.next || !k) return head;
const list = [];
let len = 0;
// put linked list into array
for (let cur = head; cur; cur = cur.next) {
list[len++] = cur;
}
// calculate the break position
const newHead = len - (k % len);
if (newHead === len) return head;
// change pointer
list[len - 1].next = head;
list[newHead - 1].next = null;
return list[newHead];
};
Without extra space
If you don't want to use extra space, then we need to traverse again to get the new tail node.
Here's a sample code from me:
const rotateRight = (head, k) => {
if (!head || !head.next || !k) return head;
let newTail = head;
let tail = head;
let len = 1;
// get current tail node and length of linked list
while (tail.next) {
tail = tail.next;
++len;
}
// link current tail to head
tail.next = head;
// get the new tail node
for (let i = 1; i < len - (k % len); ++i) {
newTail = newTail.next;
}
const ret = newTail.next;
// change it into the real tail
newTail.next = null;
return ret;
};That’s all folks! In this post, we solved LeetCode problem 61. Rotate List
I hope you have enjoyed this post. Feel free to share your thoughts on this.
You can find the complete source code on my GitHub repository. If you like what you learn. feel free to fork 🔪 and star ⭐ it.
In this blog, I have tried to collect & present the most important points to consider when improving Data structure and logic, feel free to add, edit, comment, or ask. For more information please reach me here
Happy coding!


Comments
Post a Comment