931. Minimum Falling Path Sum
Minimum Falling Path Sum
Given an n x n array of integers matrix, return the minimum sum of any falling path through matrix.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses the element in the next row that is either directly below or diagonally left/right. Specifically, the next element from position (row, col) will be (row + 1, col - 1), (row + 1, col), or (row + 1, col + 1).
Example 1:
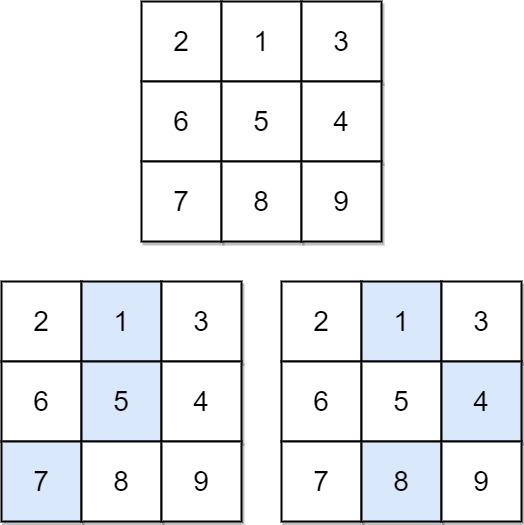
Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]] Output: 13 Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum as shown.
Example 2:
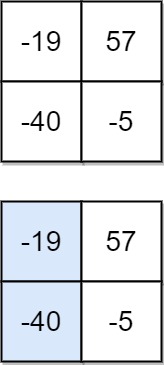
Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]] Output: -59 Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is shown.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
var minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
let m = matrix[0].length;
let min = Infinity;
// base case - when i will be 0, dp[0][j] will be matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++) matrix[0][j] = matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0 ; j < m; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, compute(n - 1, j, matrix));
}
return min;
};
function compute(i, j, matrix) {
if(j < 0 || j >= matrix.length) return 10000; // big enough number
if(i === 0) return matrix[0][j];
let up = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j, matrix);
let upLeft = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j - 1, matrix);
let upRight = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j + 1, matrix);
return Math.min(up, upLeft, upRight);
}Recursion + Dynamic Programming
var minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
let m = matrix[0].length;
let min = Infinity;
let dp = new Array(n).fill(-1).map(() => new Array(m).fill(-1));
// base case - when i will be 0, dp[0][j] will be matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++) matrix[0][j] = matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0 ; j < m; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, compute(n - 1, j, matrix, dp));
}
return min;
};
function compute(i, j, matrix, dp) {
if(j < 0 || j >= matrix.length) return 10000; // big enough number
if(i === 0) return matrix[0][j];
if(dp[i][j] !== -1) return dp[i][j];
let up = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j, matrix, dp);
let upLeft = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j - 1, matrix, dp);
let upRight = matrix[i][j] + compute(i - 1, j + 1, matrix, dp);
return dp[i][j] = Math.min(up, upLeft, upRight);
}Dynamic Programming + Tabulation
var minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
let m = matrix[0].length;
let dp = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(m).fill(0));
// tabulation // bottom-up approach
// base case - when i will be 0, dp[0][j] will be matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++) dp[0][j] = matrix[0][j]
for(let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(let j = 0 ; j < m; j++) {
let up = matrix[i][j] + dp[i - 1][j];
let upLeft = matrix[i][j];
if((j - 1) >= 0) upLeft += dp[i - 1][j - 1]; // if not out of bound
else upLeft += 10000; // big enough number
let upRight = matrix[i][j];
if((j + 1) < m) upRight += dp[i - 1][j + 1]; // if not out of bound
else upRight += 10000; // big enough number
dp[i][j] = Math.min(up, upLeft, upRight);
}
}
return Math.min(...dp[n - 1]);
};Dynamic Programming + Tabulation (Space optimized)
var minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
let m = matrix[0].length;
let prev = new Array(m).fill(0);
let curr = new Array(m).fill(0);
// tabulation // bottom-up approach
// base case - when i will be 0, dp[0][j] will be matrix[0][j]
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++) prev[j] = matrix[0][j];
for(let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(let j = 0 ; j < m; j++) {
let up = matrix[i][j] + prev[j];
let upLeft = matrix[i][j];
if((j - 1) >= 0) upLeft += prev[j - 1]; if not out of bound
else upLeft += 10000; // big enough number
let upRight = matrix[i][j];
if((j + 1) < m) upRight += prev[j + 1]; // if not out of bound
else upRight += 10000; // big enough number
curr[j] = Math.min(up, upLeft, upRight);
}
prev = curr;
}
return Math.min(...prev);
};Tabulation
const minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let m = matrix.length;
let n = matrix[0].length;
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][j] + Math.min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i - 1][j - 1] || 10000, matrix[i - 1][j + 1] || 10000);
}
}
return Math.min(...matrix[m - 1]);
};That’s all folks! In this post, we solved LeetCode problem 931. Minimum Falling Path Sum
I hope you have enjoyed this post. Feel free to share your thoughts on this.
You can find the complete source code on my GitHub repository. If you like what you learn. feel free to fork 🔪 and star ⭐ it.
In this blog, I have tried to collect & present the most important points to consider when improving Data structure and logic, feel free to add, edit, comment, or ask. For more information please reach me here
Happy coding!


Comments
Post a Comment